Delegation | Task Offloading
Let's add basic analytics to our blog (just taking an example, assume Medium/Hashnode). So the whole idea is, the crux of designing a good system at scale is minimize the number of synchronous calls you are making.
The mantra for performance: What does not need to be done in real time should not be done in real time. If you can somehow delegate and do async processing, do it async.
We write to log and forget about it. That's how Postgres does commits. So that's what gives you consistent commit times. But then it puts additional load on the background processing, there's different volume altogether. But try to minimize things that you are doing synchronously so that you wrap up things as fast as possible.
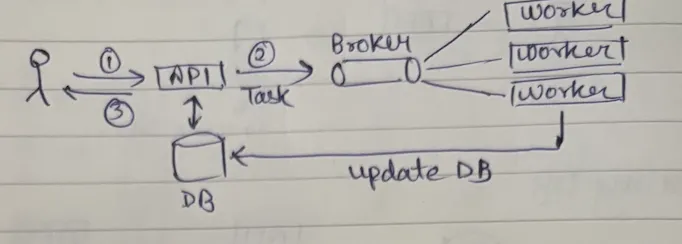
Now a classic example of this you all know is creation of EC2 instance or trans-coding of video files. It takes a long time and for that long time you cannot have that HTTP request open. For example, let's say you requested to create an EC2 instance, you made a POST request and it takes let's say five minutes (it doesn't take that long but assume it takes five minutes) - your HTTP request cannot wait for this long, it would start timing out depending on your web server and your load balancer configuration. Plus why keep your request waiting?
Which is where you typically see a flow where you have a long running task - you put the task in the broker and let async workers pick that up and update the database with the status. So this is what your delegation is all about.
The core idea: Delegate & Respond
Tasks that are Delegated
Tasks that should outlive your request timeout:
- Long running tasks (spin up EC2 / video encoding)
- Heavy computation queries
- Batch & write operations
- Anything that could be eventual
Brokers
The key infra component that enables this is a broker. Broker is a generic term - it's a buffer to keep the tasks & messages.

This broker can be of two types:
- Message Queues
- Message Streams
Message Queues (Example: SQS, RabbitMQ)
- Think of it like a to-do list where each task gets crossed off once someone completes it
- Message is consumed → processed → deleted (gone forever)
- One message = one consumer processes it
- Good for: "Hey, send this email" or "Process this payment"
Visibility timeout concept - a mechanism designed to prevent multiple consumers from processing the same message simultaneously and to handle message processing failures
1. Worker A picks up message: "Increment blog count for user 123"
2. Queue hides this message from other workers (visibility timeout starts)
3. If Worker A crashes and doesn't delete the message within timeout
4. Queue makes the message visible again
5. Worker B picks it up and processes it again
6. Result: Blog count gets incremented twice! (Bug!)
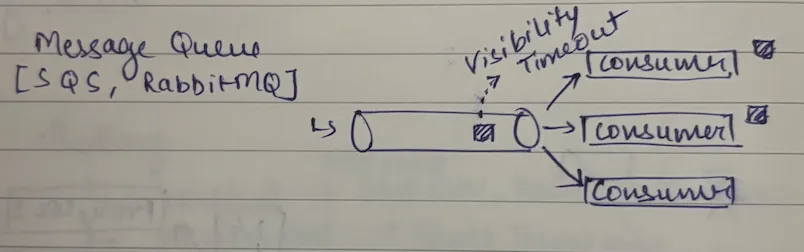
Homogeneous consumers: Any consumer can handle any message
Message Streams (Example: Kafka, Kinesis)
- Think of it like a journal/log that multiple people can read
- Message stays in the stream even after being read
- One message = multiple consumer groups can read the same message
- Good for: "A blog was published" (search team indexes it, analytics team counts it, notification team sends alerts)
Consumer groups concept - different types of consumers can consume the same message for different purposes.
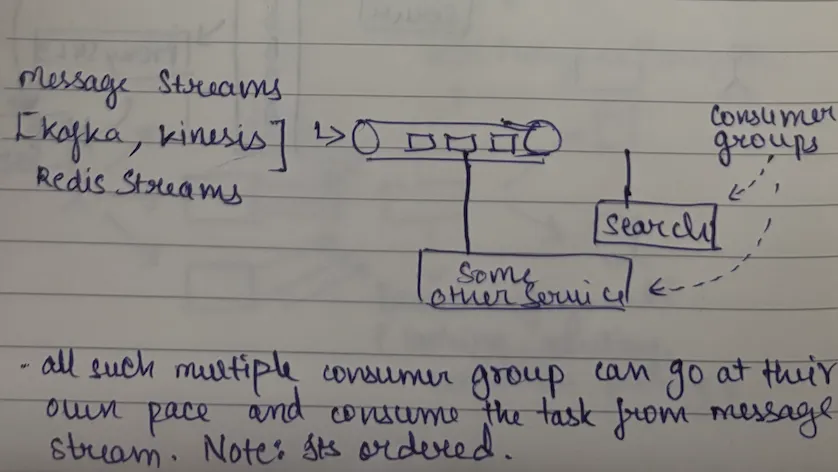
Heterogeneous consumers: Same message consumed by different consumer groups
| Scenario | Queue or Stream? | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Send welcome email | Queue | One-time task, should happen exactly once |
| User registered | Stream | Multiple services care: send email, update analytics, create profile |
| Process video upload | Queue | Heavy task, any worker can handle |
| Order placed | Stream | Payment, inventory, shipping, analytics all need to know |
| Delete spam comment | Queue | Simple task, happens once |
| User viewed article | Stream | Analytics, recommendations, ads all interested |
Real Example: Blog Analytics
Let's take a concrete example. Let's say in case of a blog (like Medium), what you want to do is maintain a count of total number of blogs published by a user.
You have two ways to do it: https://tautik.me/scaling-db-proxy-pattern/
- Synchronously - every time a blog is published I do
total_blogs++ - Asynchronously - our way

The Async Way
It's a crude example, very primitive example but it will help you build an understanding. In case of this, you want to do it in async fashion. What you can do is:
Whenever a blog is published → You put a message in SQS → A worker picks that up → That worker does total_blogs++ in the database.
UPDATE users SET total_blogs = total_blogs + 1 WHERE id = user_id;
Instead of calculating data on-demand (like counting a user's total blogs by JOINing users and blogs tables every time someone views their profile), we store the calculated result directly in the database (like a total_blogs column in the users table). This way, displaying the count becomes a simple, fast lookup rather than an expensive calculation that gets slower as data grows. Trade-off: We accept slight data lag (count updates asynchronously) in exchange for lightning-fast reads.
So this way you accept a lag in processing and data getting reflected here rather than doing a synchronous message. So the opposite is sync vs async.
The Problem with Single Worker
Now imagine today you have this but a new requirement came where you said "Hey I need to index a blog when it's published in my search engine." Let's say use Elasticsearch for that.
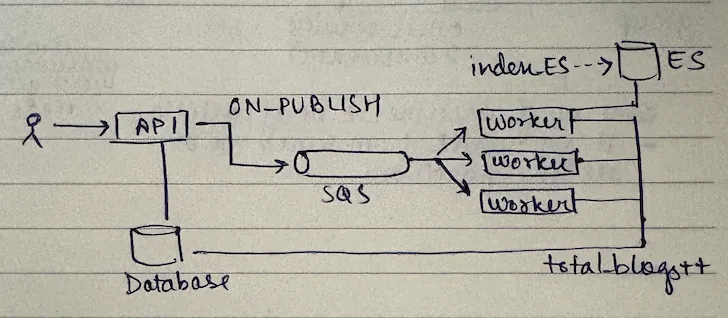 So what you have is - you not only have to do
So what you have is - you not only have to do total_blogs++, you also have to index the same thing in Elasticsearch. It's two things:
total_blogs++- Index it in Elasticsearch
So now this worker is now doing two things. This is not a good design, because:
- Worker doing
total_blogs++& index on ES - no separation of concern - Seems like two separate teams should be working on this
Problems:
- Inconsistent data - If your code broke after incrementing the count, your worker could not delete the message. After visibility timeout the message will resurface again, some other worker might pick that up and execute the same thing again. So it would do
count++again. Although you have 5 blogs but system will now say 6 blogs because this happened twice. - Team dependencies - This codebase which does count increment and ES indexing is now owned by two teams: backend team and search team. Backend team wants to push something but search team says "hey we have a broken change in master please don't push it." It's difficult to work with people, easier to work with machines.
Hence, we use Kafka
Same event consumed by two types of consumers.
The whole idea of message stream is simple - you have a Kafka topic and you have heterogeneous set of consumers which means the same message needs to be consumed by two different types of consumers (we call them consumer groups).
- Search consumer group (may contain multiple consumers, homogeneous within this consumer group)
- Backend consumer group (doing
total_blogs++)
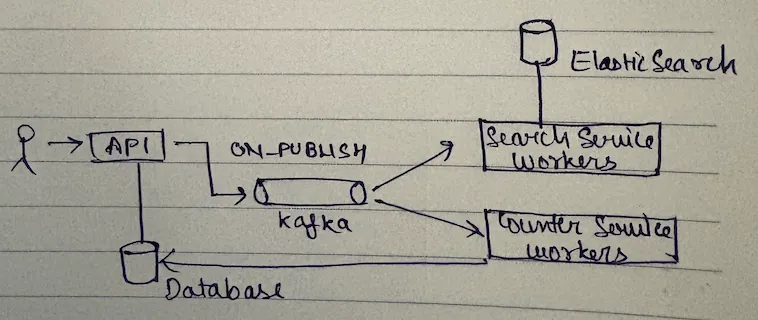
What you need to do is whenever this event (blog is published) happens, you create that event and now two consumer groups consume it:
- Search consumer group does ES indexing
- Backend consumer group does
total_blogs++
The best way to visualize Kafka is that all the messages are enqueued in the queue (which is a Kafka topic) and then the consumers iterate at their own sweet pace on the messages. It's possible that one iterates faster than the other, it doesn't matter. So system becomes eventually consistent - it's not strongly consistent that search and count both happen at the same time, but eventually everything would be consistent.
This is consumer group - so this is the fundamental difference between message queues and message streams.
Read about Kafka Essentials: https://tautik.me/kafka/